本文最后更新于:23 天前
Palette
- Vibrant (充满活力的)
- Vibrant dark (充满活力的黑)
- Vibrant light (充满活力的亮)
- Muted (柔和的)
- Muted dark (柔和的黑)
- Muted light (柔和的亮)
implementation 'androidx.palette:palette:1.0.0'Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.color_size);
Palette.from(bitmap).generate(palette -> {
assert palette != null;
Palette.Swatch swatch = palette.getVibrantSwatch();
assert swatch != null;
int color = swatch.getRgb();
});禁用多窗口模式
当 targetSdkVersion 设置的值不小于 24 时:
<application> ... android:resizeableActivity="false" ... </application>当 targetSdkVersion 设置的值小于 24 时,
android:resizeableActivity属性不会生效,此时设置应用不支持横竖屏切换android:screenOrientation="portrait"(在清单文件的<activity>元素中设置) 即可。
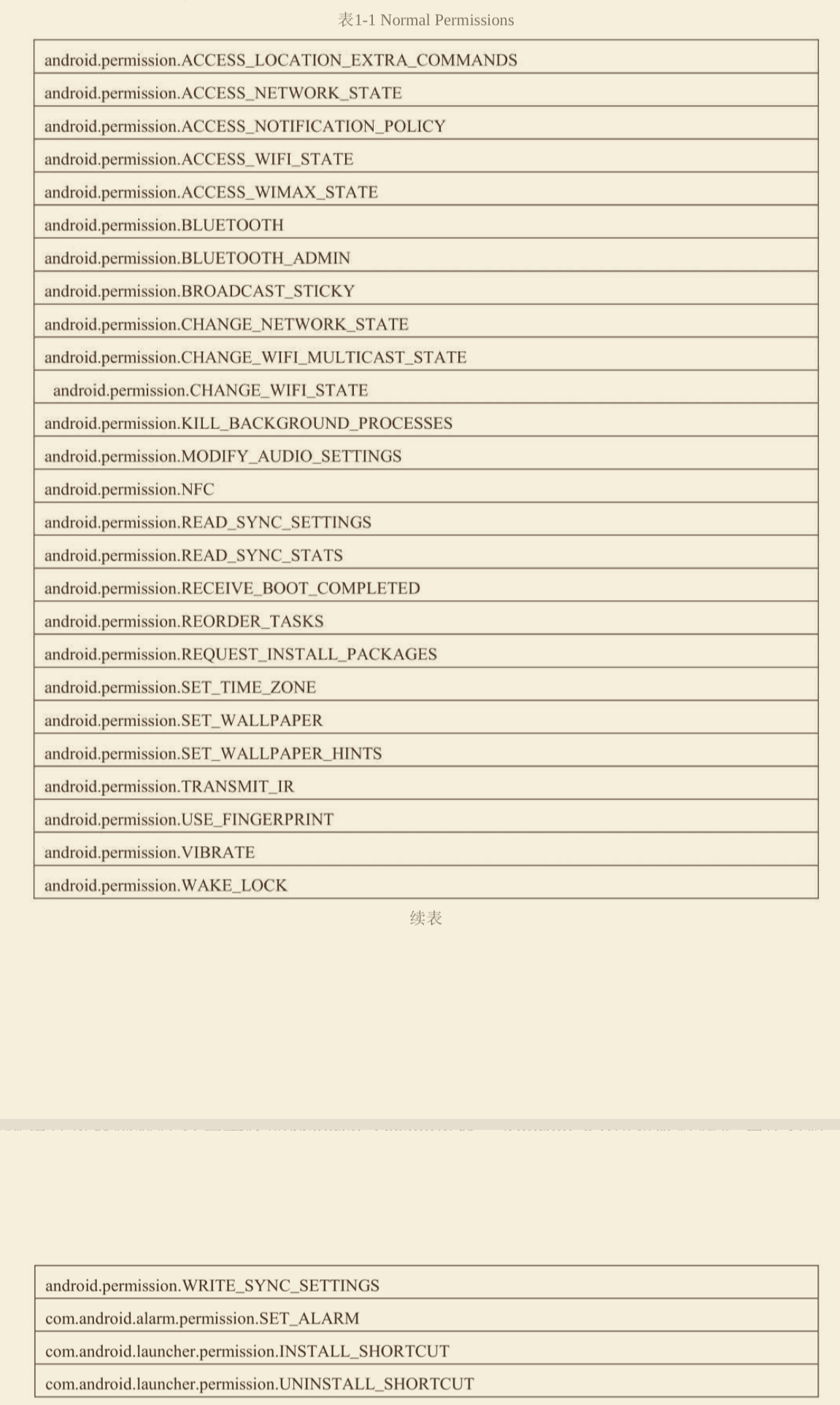
权限

Material Design 控件及布局
TextInputLayout
其子元素只能为 EditText
setErrorEnabled(true)setError(String message)
TabLayout
AppBarLayout 布局内嵌元素 Toolbar 和 TabLayout
TabLayout 属性
app:tabMode="scrollable"设置 Tab 的模式为可滑动的app:tabMode="fixed"设置 Tab 固定不可滑动tabIndicatorHeight设置底部指示器的高度tabIndicatorColor设置底部指示器的颜色
NavigationView
app:headerLayout=""引入头部文件app:menu=""引入菜单布局
CoordinatorLayout 实现 Toolbar 隐藏效果
Toolbar 中 app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways" 属性设置滚动事件,属性里必须至少启用 scroll 这个 flag,这个 View才会滚出屏幕,否则它将一直固定在顶部。
CollapsingToolbarLayout
app:contentScrim=""设置 CollapsingToolbarLayout 收缩后最顶部的颜色app:enpandedTitleGravity="left|bottom"将 CollapsingToolbarLayout完全展开后,title 所处的位置,默认为left|bottomapp:collapsedTitleGravity="left"当头部的衬图 ImageView 消失后,此 title 将回归到 Toolbar 的位置,默认为leftapp:layout_scrollFlags=""设置滚动事件,属性里面必须至少启用scroll,这样当前 View 才会滚动出屏幕scroll|exitUntilCollapsed折叠scroll|enterAlways隐藏
特殊字符串资源 @string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior 和 AppBarLayout.ScrollingViewBehavior 相匹配,用来通知 AppBarLayout 何时发生了滚动事件,此 Behavior 需要设置在触发事件的 View 上,比如 RecyclerView、NestedScrollView。当然,AppBarLayout 中的子 View 需要设置 app:layout_scrollFlags 属性。
第3章 View 和自定义 View
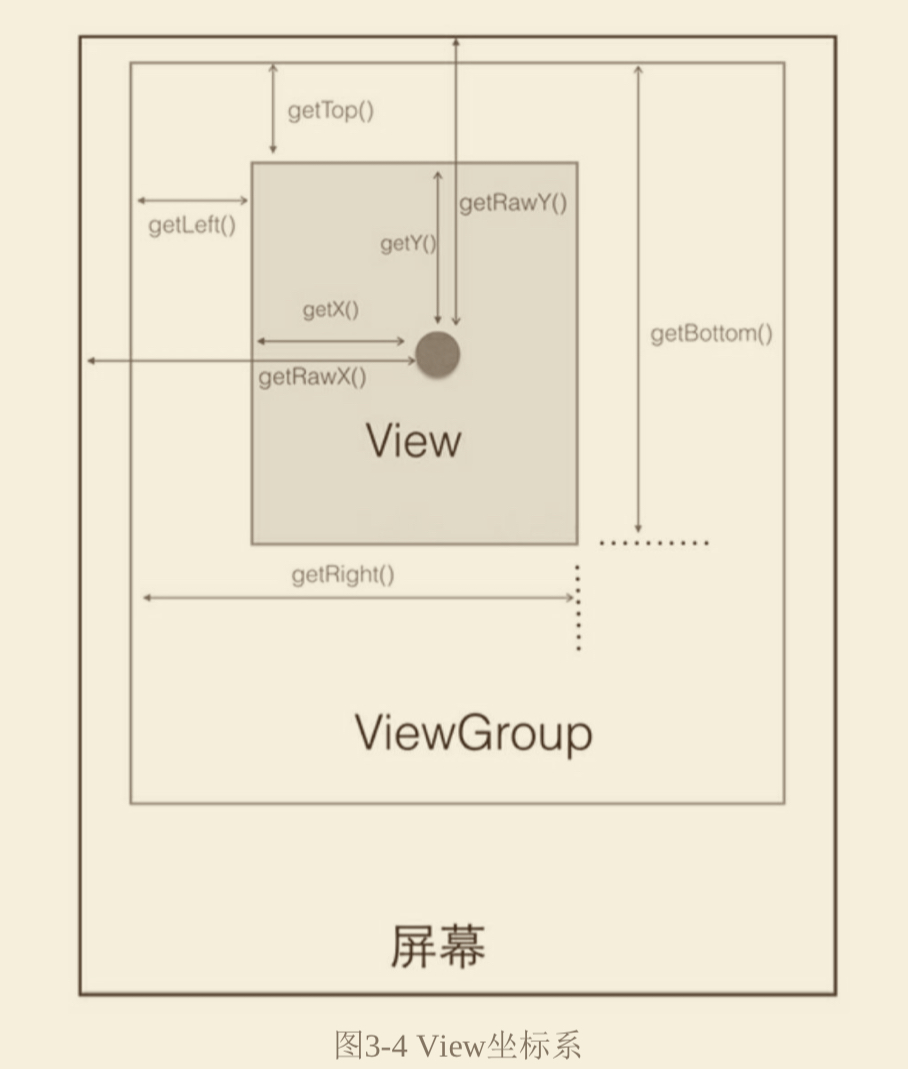
坐标系
View 的滑动
layout()offsetLeftAndRight()和offsetTopAndBottom()LayoutParams(改变布局参数)scrollTo()和scrollBy()Scroller
Scroller 本身不能实现 View 的滑动,需要与 View 的computeScroll()方法配合实现弹性滑动效果
属性动画
四种动画:Alpha、Rotate、Translate、Scale
- ObjectAnimator
- translationX 和 translationY:沿着 X 轴或 Y 轴移动
- rotatioin 和 rotationX 和 rotationY:围绕 View 的支点进行旋转
- PrivotX 和 ProvitY:控制 View 对象的支点位置,默认该支点位置就是 View 对象的中心
- alpha:
- 透明度,默认是 1(不透明),0 代表完全透明
- x 和 y:描述 View 对象在其容器中的最终位置
- ValueAnimator
- AnimationSet
View 的事件分发机制
dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)用来进行事件的分发onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)用来进行事件的拦截,在dispatchTouchEvent()中调用onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)用来处理点击事件,在dispatchTouchEvent()中调用
当点击事件产生后会由 Activity 来处理,传递给 PhoneWindow,再传递给 DecorView,最后传递给顶层的 ViewGroup。一般在事件传递中只考虑 ViewGroup 的 onInterceptTouchEvent() 方法。对于根 ViewGroup,点击事件首先传递给它的 dispatchTouchEvent() 方法,如果 ViewGroup 的 onInterceptTouchEvent() 方法返回 true,则表示它要拦截这个事件,这个事件就会交给它的 onTouchEvent() 方法处理,如果 onInterceptTouchEvent() 方法返回 false,则表示它不拦截这个事件,则这个事件会交给它的子元素的 dispatchTouchEvent() 来处理,如此反复。如果传递给底层的 View,View 是没有子 View 的,就会调用 View 的 dispatchTouchEvent() 方法,一般情况下最终会调用 View 的 onTouchEvent() 方法。
当点击事件传给底层的 View 时,如果其 onTouchEvent() 方法返回 true,则事件由底层的 View 消耗并处理;如果返回 false 则表示该 View 不做处理,则传递给父 View的 onTouchEvent() 处理;如果父 View 的 onTouchEvent() 仍旧返回 false,则继续传递给该父 View 的 父 View 处理,如此反复下去。
View 的工作流程
- measure 测量 View 的宽和高
- layout 确定 View 的位置
- draw 绘制 View
第4章 多线程编程
线程基础
- 实现 Callable 接口,重写
call()方法 Thread.interrupt()请求中断线程Thread.interrupted()对中断标识位进行复位Thread.currentThread.isInterrupted()判断线程是否被置位- 不要在底层代码里捕获
InterruptedException异常后不做处理,最好不使用 try 语句捕获这样的异常
同步
synchronized- 重入锁
ReentrantLock - 每一个对象有一个内部锁,并且该锁有一个内部条件。
- 并发编程中的 3 个特性:原子性、可见性、有序性
线程池
/**
* ThreadPoolExecutor 类一共有 4 个构造方法,这是参数最多的一个
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程数
* @param maximumPoolSize 线程池允许创建的最大线程数
* @param keepAliveTime 非核心线程闲置的超时时间。如果设置 allowCoreThreadTimeOut 属性为 true, 这个参数也会应用到核心线程上
* @param unit keepAliveTime 参数的时间单位
* @param workQueue 任务队列
* @param threadFactory 线程工厂。可以用线程工厂为每个创建出来的线程设置名字。一般情况下无需设置
* @param handler 饱和策略
*/
public void ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
...
}饱和策略默认为 AbordPolicy,表示无法处理新任务,并抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,此外还有 3 种策略:
CallerRunsPolicy
用调用者所在的线程来处理任务。此策略提供简单的反馈控制机制,能够减缓新任务的提交速度。DiscardPolicy
不能执行的任务,并将该任务删除。DiscardOldestPolicy
丢弃队列最近的任务,并执行当前的任务。
线程池的处理流程和原理
graph LR
A[提交任务] --> B{线程数是否<br/>达到 corePoolSize}
B --否--> C[创建核心<br/>线程执行任务]
B --是--> D{任务队列<br/>是否已满}
D --否--> E[将任务加在<br/>任务队列中]
D --是--> F{线程数是否<br/>达到最大线程数}
F --是--> I[执行饱和策略]线程池的种类
FixedThreadPool
可重用固定线程数的线程池,只有数量固定的核心线程。keepAliveTime 设置为 0L,多余的线程会被立即终止。CachedThreadPool
根据需要创建线程的线程池,没有核心线程。keepAliveTime 设置为 60L。SingleThreadExecutor
使用单个工作线程的线程池,只有一个核心线程。ScheduledThreadPool
实现定时和周期性任务的线程池。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!